Why Morphology Matters in Biotherapeutics In biotherapeutic development—whether monoclonal antibodies, cell and gene therapies, or complex …
Read Post
All biotherapeutics contain particulate matter, defined by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) as mobile undissolved particles that are …
Read Post
A new white paper from the Japan Biopharmaceutical Consortium provides compelling validation for what many in the field already suspect: flow imaging …
Read Post

Comprehensive characterization of biotherapeutics is often challenging, given their complexity. In many cases, singular analytical methods cannot …
Read Post

Visible particles are one of the most important sample attributes to monitor when developing and manufacturing biopharmaceuticals and other …
Read Post

Flow Imaging Microscopy (FIM) via FlowCam plays a crucial role in biotherapeutic development by providing a tool for quantifying and characterizing …
Read Post

Subvisible particles (those 2-100 μm in diameter) in protein, cell, and gene therapies and other parenteral drug products pose risks to the safety …
Read Post
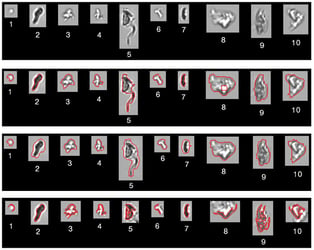
Scientists using FlowCam in biopharmaceutical research need to accurately assess many diverse particle types that may be present in their samples. …
Read Post

Strategies for monitoring subvisible particles in biopharmaceutical formulations are central to developing and manufacturing safe, effective drug …
Read Post

Assessing subvisible particle content is a required quality control step for biotherapeutics and other parenteral drug products. The United States …
Read Post

All types of biotherapeutics, ranging from protein therapies to cell and gene therapies, contain particles. While the types of particles can vary …
Read Post
One of the main values of using flow imaging microscopy (FIM) when analyzing pharmaceuticals is the method's sensitivity to transparent particles. …
Read Post